Virtual Filesystem
The Virtual Filesystem (VFS) lets you use images, videos, fonts, 3D models, and other assets in your patches. Files can be embedded in the patch or linked from your local system.
Managing Files
Use the sidebar to manage your files. Open it with Ctrl/Cmd + B > Files or click "Open Sidebar" in the bottom right.
See Files for more details on file management.
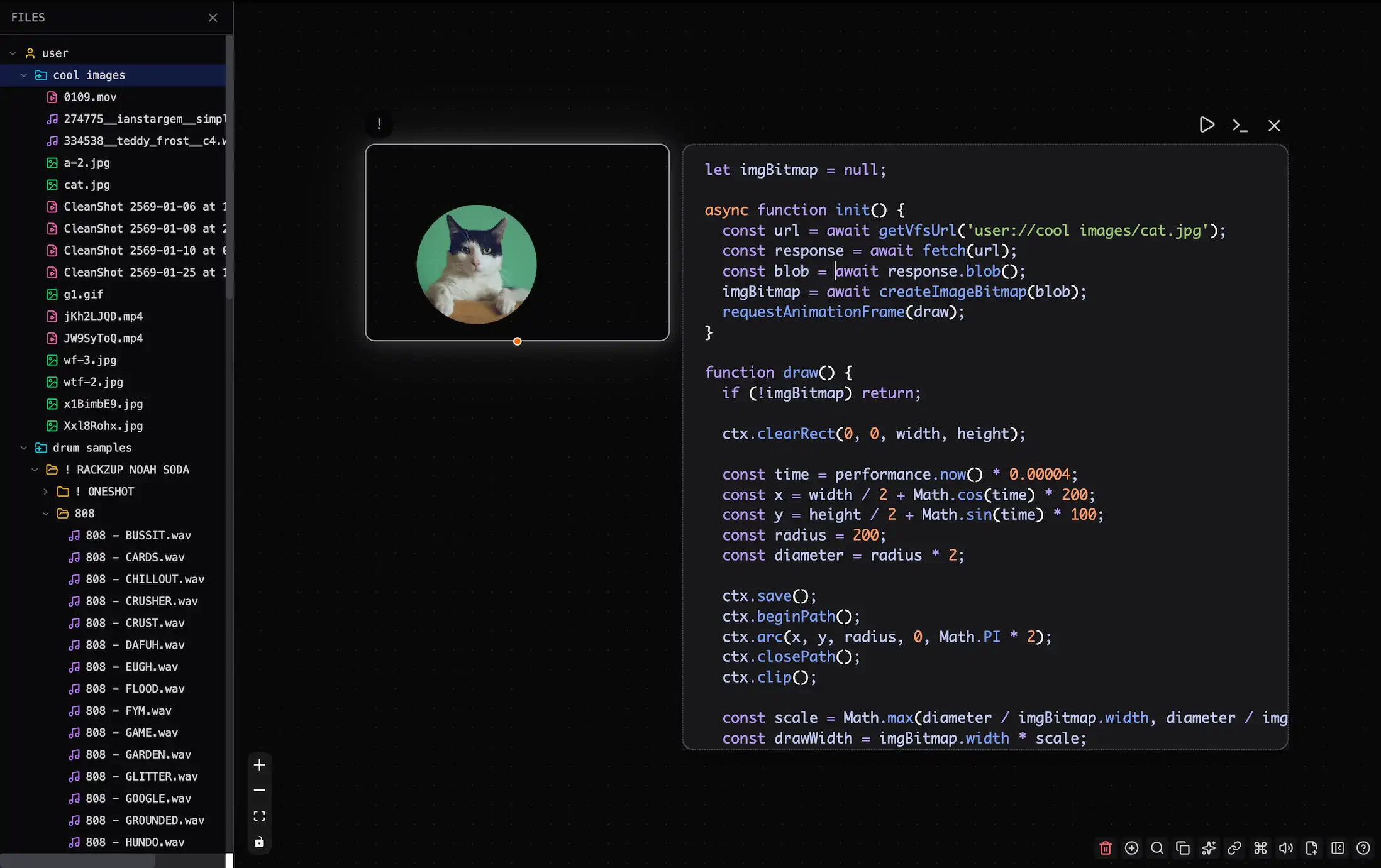
Loading Files in Code
Use await getVfsUrl(path) to get a URL for any file in the VFS:
// In p5:
let img;
async function setup() {
let url = await getVfsUrl("user://photo.jpg");
img = await loadImage(url);
}
// In js or canvas.dom:
const url = await getVfsUrl("user://data.json");
const data = await fetch(url).then(r => r.json());
VFS paths use the user:// prefix for user-uploaded files. Object URLs are automatically cleaned up when the object is destroyed.
Getting File Content
To get the underlying Blob or raw data:
// Get as Blob
const blob = await fetch(await getVfsUrl("user://image.png")).then(r => r.blob());
// Get as ArrayBuffer (for binary data)
const buffer = await fetch(await getVfsUrl("user://audio.wav")).then(r => r.arrayBuffer());
// Get as text
const text = await fetch(await getVfsUrl("user://data.csv")).then(r => r.text());
Supported Objects
The getVfsUrl() function is available in all JavaScript Runner objects.
See Also
- Files - Managing files in the sidebar
- JavaScript Runner - Full JSRunner API reference
- Data Storage - Persistent key-value storage